
|
Highlights
-
Mozambique maize exports into Malawi account for three quarters of recorded informal trade.
-
Ease of access by Mozambican farmers to markets in southern Malawi and absence of undue government interference on informal trade spurs Mozambique - Malawi trade.
-
Maize trade is structured and competitive, and prices are set largely by supply and demand forces.
Mozambique – Malawi Exports Dominate Regional Informal Cross Border Trade
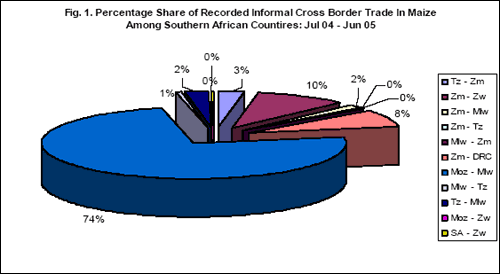
Mozambique’s informal maize exports to Malawi dominate the informal food trade among seven Southern African countries that include the Democratic Republic of Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, South Africa, Zambia and Zimbabwe. Mozambique’s maize exports to Malawi account for 74% of the captured trade since monitoring began in July 2004; and its share of the trade is likely to be higher in the current marketing season (89% so far) compared with last season (70%) as Zambia (last season’s second major exporter), has since imposed a maize export ban due to a poor harvest.
 |
| Source: FEWS NET and WFP Malawi; TSC |
In order to understand the trade dynamics between southern Malawi and northern Mozambique, the Southern Africa informal cross border food trade monitoring initiative in conjunction with FEWS NET Malawi and Mozambique, and the Agriculture Information Service of Mozambique’s Ministry of Agriculture (SIMA) recently conducted a rapid assessment mission at the Milange (Mozambique) and Muloza (Malawi) border point and at Mandimba (Mozambique) and Kalanje (Malawi) border point. The two border points contribute the highest volumes of trade between the two countries.
 |
| Figure 1: Cyclists transporting maize from Milange (Mozambique) to Muloza (Malawi) |
|
|






