
|
Inside this issue:
-
Summary of maize trade flows
-
Maize price trends
-
Formal exports from South Africa
-
Summary of trade in rice and beans
-
Summary tables
-
Summary tables and Map
Overall summary of trade flows
The volume of informal cross border trade in maize, rice and beans captured by the Southern Africa Informal Cross Border Food Trade monitoring system since the beginning of the marketing season in April 2006 has reached nearly 78,000 MT – 30% below the 111,000 MT recorded during the same period last year.
| Figure 1: Recorded Informal Cross Border Maize Trade in DRC, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa Tanzania, Zambia & Zimbabwe |
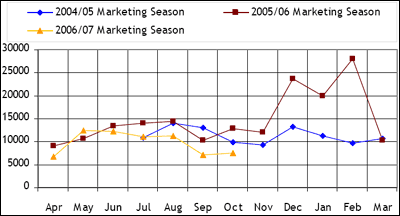
|
The decline in overall volumes traded this year is attributed to better harvests in two of last season’s major importing countries, Malawi and Zambia (both countries have declared grain surpluses). Zimbabwe, the other major importing country with a deficit this season, has not attracted much informal cross border activity as
the other countries due to its restrictions on the trade. On the basis of the trend established over the past two seasons,
lean season demand (November to February) usually stimulates some resurgence in overall volumes traded, particularly maize. It is
therefore, anticipated that volumes traded will rise over the next couple of months to meet this demand although the resurgences are likely to be moderate. On commodity by commodity basis, between April and October this year, maize is the most dominant commodity being traded and accounts for 88% of the overall trade captured while rice and beans account for 5% and 7% respectively. Last year at the same time, trade in maize accounted for 76% of the overall trade where as rice and bean trade accounted for 14% and 10% of the trade respectively.
| Figure 2: Recorded Informal Cross Border Food Trade in Rice & Beans DRC, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa
Tanzania, Zambia & Zimbabwe |
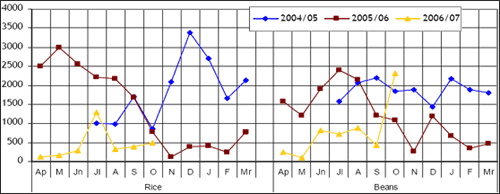
|
|
|






