
|
Overall summary of trade flows
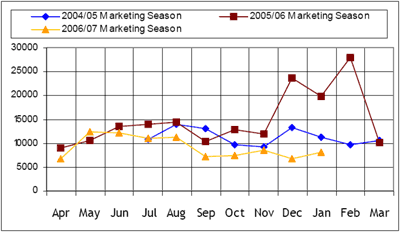
Figure 1: Recorded Informal Cross Border Maize Trade in DRC, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa Tanzania, Zambia & Zimbabwe
By the end of January, close to 107,200 MT of trade in maize (92,000 MT), rice (5,800 MT) and beans (9,400 MT) had been captured by the Southern Africa informal cross border food trade monitoring system since the start of the marketing season in
April 2006. The combined volume of trade in all the three commodities is 37% down on the amount captured during a similar
period in the last season. On commodity by commodity basis, the volume of maize traded is down by 34%; rice trade is down
63% and bean trade is down 30 per cent. About 80% of the maize captured (74,000 MT) was exported to Malawi by Mozambique.
The DRC was the second largest importer (from Zambia) accounting for 6% of the trade followed by Zambia (importing from Tanzania) at 5%. Trade in rice was led by exports from Mozambique to Malawi (1,700 MT), followed closely by exports from Zambia (1,500 MT) to the DRC. Meanwhile Malawi imported 63% of total beans traded, comprising 2,800 MT of the imports from Mozambique and 3,000 MT from Tanzania. The DRC was the second largest importer of beans (from Zambia) accounting for 24% of the trade.
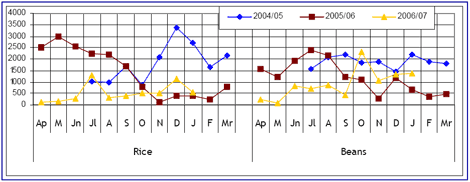
Figure 2: Recorded Informal Cross Border Food Trade in Rice & Beans DRC, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa Tanzania, Zambia & Zimbabwe
|
|






